🔰 SECTION 0 — Redis Fundamentals (Before Any Commands)¶
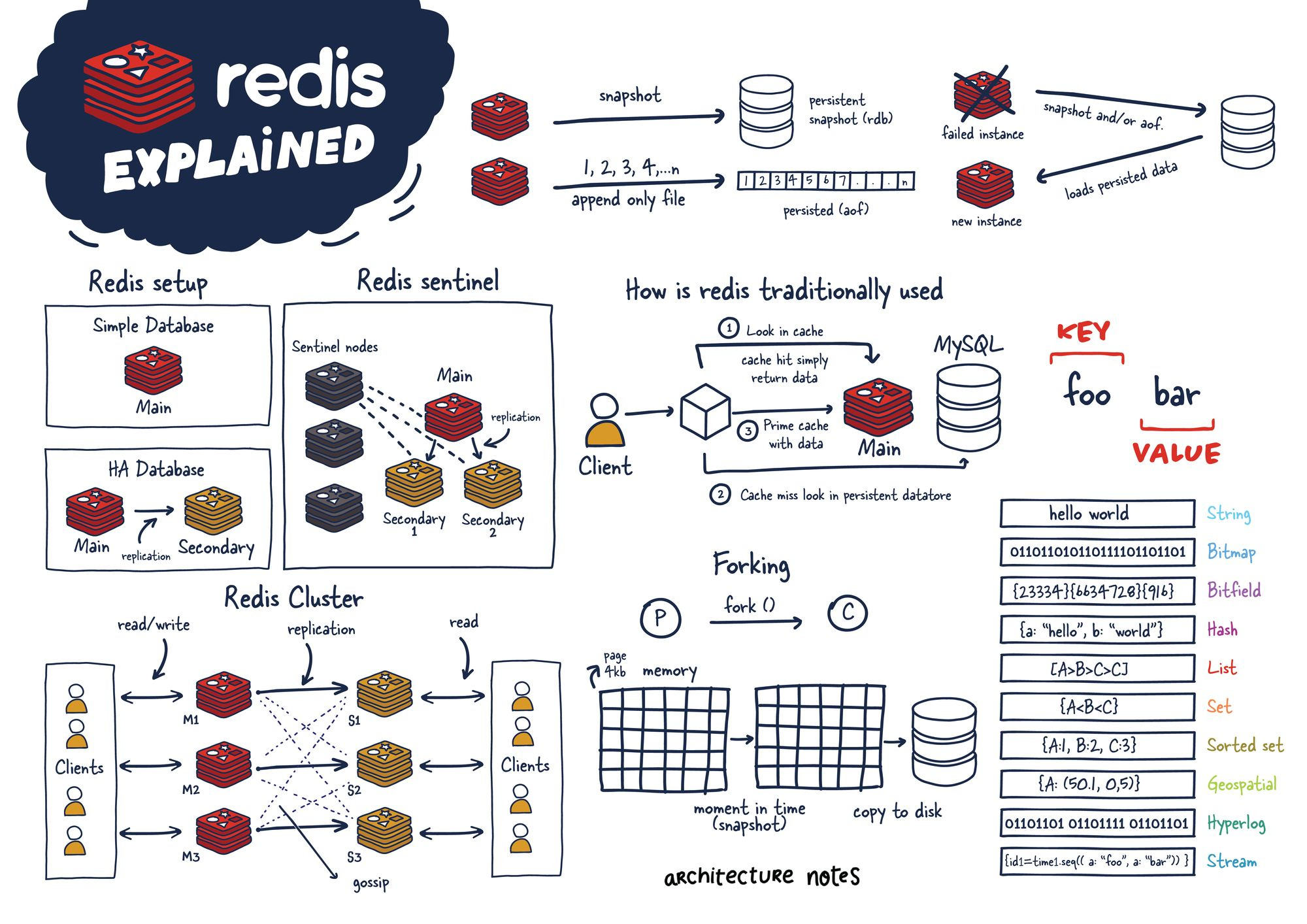
🧠 What Redis really is (important)¶
Redis is:
- A single-threaded event loop
- Holding data entirely in RAM
- Persisting to disk optionally
- Optimized for very fast reads/writes
Redis is fast because it avoids locks and disk I/O
🧩 Internal mental model¶
KEY (string)
↓
Value (string | hash | list | set | zset | stream)
↓
Stored in RAM
↓
Optional persistence to disk
🔌 Start & Connect (once)¶
Test:
Redis replies:
Meaning:
Redis event loop is alive and accepting commands
1️⃣ STRING — The Atomic Unit of Redis¶
🧠 Why strings exist¶
Strings are:
- The fastest Redis type
- Atomic (safe for counters)
- Used in 90% of Redis use cases
Real-world uses¶
- Cache values
- Session tokens
- Feature flags
- Counters
- Locks
🧩 How Redis stores a string¶
Internally:
- Key is always a string
- Value is a byte array
- TTL stored separately
🧪 Step-by-step¶
Step 1 — Store value¶
Redis does:
- Allocates memory
- Stores key hash
- Stores value bytes
Step 2 — Read value¶
Redis:
- Hashes key
- Direct memory lookup
- Returns value
Step 3 — Add TTL (CRITICAL)¶
🔍 What happens internally:
- Redis adds expiry metadata
- Key auto-deletes after TTL
Why TTL matters:
Redis will crash if you forget TTLs in cache-heavy systems
Step 4 — Atomic counter¶
Why INCR is special:
- No race condition
- Single-threaded atomic op
Used for:
- Rate limiting
- Analytics
- Quotas
🚫 DON’T
- Store large JSON blobs
- Use strings without TTL for cache
2️⃣ HASH — Structured Data Without JSON¶
🧠 Why hashes exist¶
Hashes solve:
- Storing structured data
- Updating single fields
- Avoiding JSON parsing
Real-world uses¶
- User profiles
- Product metadata
- Configuration
🧩 Internal model¶
Redis stores fields compactly → memory efficient.
🧪 Step-by-step¶
Step 1 — Create hash¶
Redis:
- Creates hash table
- Stores fields separately
Step 2 — Read data¶
Why hashes are fast:
- Field lookup is O(1)
Step 3 — Update one field¶
Only role changes — no full rewrite.
Step 4 — Expiry on hash¶
⚠ TTL applies to entire hash, not fields.
🚫 DON’T
- Store nested JSON in hashes
- Use hashes without TTL in cache
3️⃣ LIST — Ordered Queue / Stack¶
🧠 Why lists exist¶
Lists solve:
- Queues
- Background jobs
- Message buffering
Real-world uses¶
- Job queues
- Email sending
- Event buffering
🧩 Internal model¶
Linked list internally → fast push/pop.
🧪 Step-by-step¶
Step 1 — Push jobs¶
Step 2 — View list¶
Step 3 — Pop job (worker)¶
FIFO achieved by:
Step 4 — Blocking pop (IMPORTANT)¶
Meaning:
- Worker waits
- No CPU waste
- Production-safe
🚫 DON’T
- Use lists for durable queues
- Use lists without monitoring length
4️⃣ SET — Fast Membership & Uniqueness¶
🧠 Why sets exist¶
Sets solve:
- Uniqueness
- Membership checks
- Grouping
Real-world uses¶
- Online users
- Feature flags
- Permissions
🧩 Internal model¶
Unordered hash set:
🧪 Step-by-step¶
Membership check is O(1) — extremely fast.
Set math (powerful)¶
Used for:
- Access control
- A/B testing
🚫 DON’T
- Expect ordering
- Store huge sets without memory limits
5️⃣ SORTED SET — Ranking & Time-Based Logic¶
🧠 Why sorted sets exist¶
Sorted sets solve:
- Ranking
- Priority
- Time ordering
Real-world uses¶
- Leaderboards
- Rate limiting
- Scheduling
🧩 Internal model¶
Score determines order.
🧪 Step-by-step¶
Update score¶
Used for:
- Sliding window rate limits
- Priority queues
🚫 DON’T
- Use lists for ranking
- Forget score precision
6️⃣ TTL & Expiry — Redis Safety Valve¶
🧠 Why expiry is critical¶
Redis memory is finite. TTL prevents:
- OOM crashes
- Memory leaks
🧪 Commands¶
Redis deletes keys:
- Lazily on access
- Actively via background cleanup
7️⃣ Pub/Sub — Fire-and-Forget Messaging¶
🧠 Why Pub/Sub exists¶
- Real-time fan-out
- Low latency
- No persistence
🧪 Demo¶
Terminal 1:
Terminal 2:
⚠ Message lost if no subscriber.
8️⃣ Streams — Durable Messaging (Advanced)¶
🧠 Why streams exist¶
Streams solve:
- Reliable messaging
- Event sourcing
- Replayability
🧪 Demo¶
Consumer group:
Used instead of:
- Pub/Sub
- Lists (for jobs)
9️⃣ Persistence — Data Survival¶
🧠 Redis is RAM-first¶
Persistence is backup, not primary storage.
🧪 Check config¶
Enable AOF:
🔐 10️⃣ Security Basics¶
Never expose Redis publicly.
🏁 FINAL TRUTH ABOUT REDIS¶
Redis is not a database replacement Redis is a performance accelerator