1️⃣ What is Apache Airflow?¶
Apache Airflow is a workflow orchestration platform.
Think of it as:
“A scheduler + executor that runs your jobs in the right order, at the right time, with retries and visibility.”
🧠 What You’ll Learn (Roadmap)¶
- What Apache Airflow is (mental model)
- Core Airflow components (with flow)
- Executors overview (why Celery)
- Architecture: Airflow + Celery + Redis
- Local setup (Docker-based, production-like)
- Writing DAGs (basic → real-world)
- Task distribution with Celery workers
- Monitoring, retries, backfills
- Common commands & debugging
- Best practices
What Airflow is GOOD at¶
✅ ETL pipelines ✅ Data engineering workflows ✅ Batch jobs ✅ ML pipelines ✅ Cron replacement with observability
What Airflow is NOT¶
❌ Real-time streaming ❌ Event-driven APIs ❌ Long-running services
2️⃣ Airflow Core Concepts (Very Important)¶
🔹 DAG¶
- Directed Acyclic Graph
- Python file that defines workflow
- Nodes = tasks, edges = dependencies
🔹 Task¶
- A single unit of work
- Example: run a bash command, execute Python, call API
🔹 Operator¶
- Template for a task
-
Examples:
-
PythonOperator BashOperatorDockerOperator
🔹 Scheduler¶
- Decides when tasks should run
🔹 Executor¶
- Decides how tasks are executed
3️⃣ Executors Explained (Why Celery?)¶
| Executor | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Sequential | Learning only |
| LocalExecutor | Single machine |
| CeleryExecutor | Distributed, scalable |
| KubernetesExecutor | Cloud-native |
Why CeleryExecutor?¶
- Multiple workers
- Horizontal scaling
- Reliable for production
- Industry standard
4️⃣ Architecture: Airflow + Celery + Redis¶

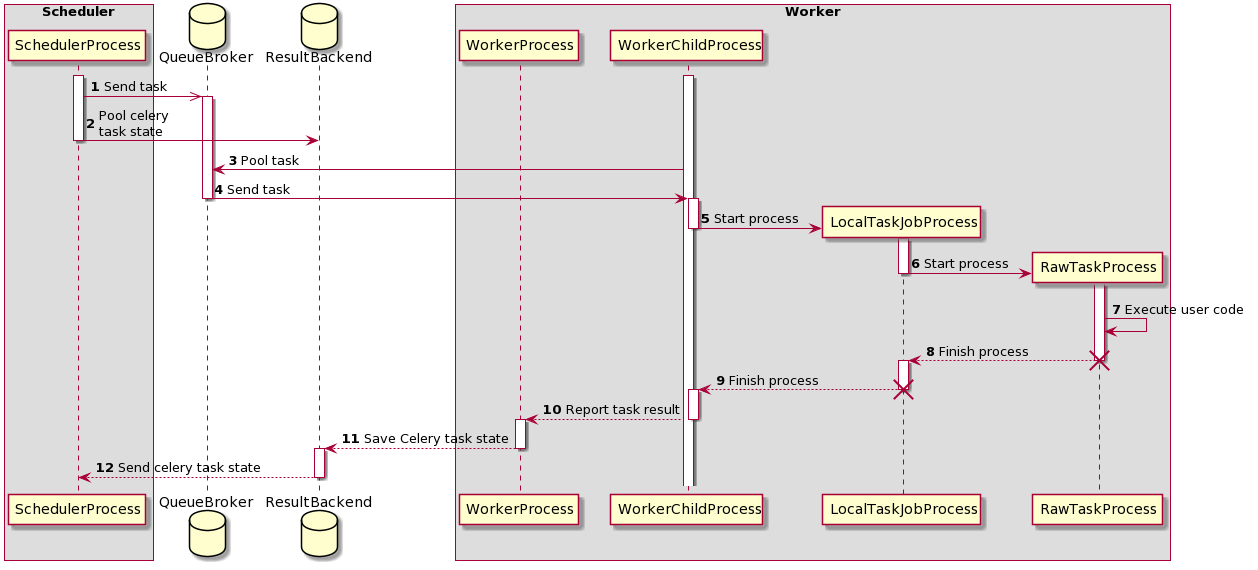
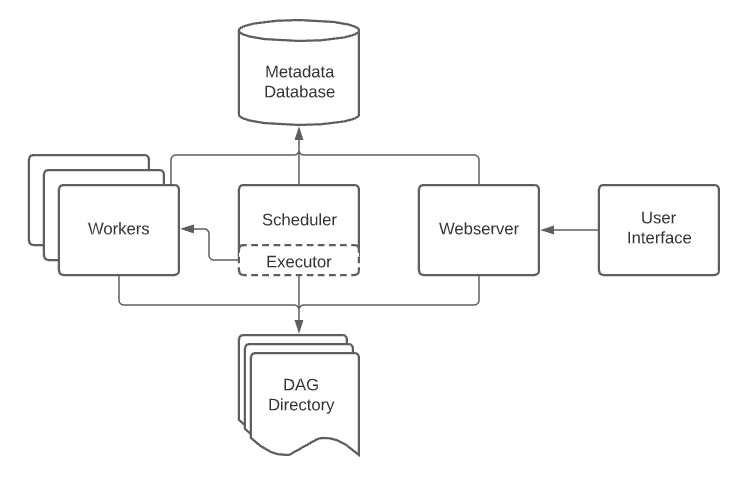
Flow (Understand this clearly 👇)¶
Components¶
| Component | Role |
|---|---|
| Webserver | UI |
| Scheduler | Schedules tasks |
| Redis | Message broker |
| Celery Workers | Execute tasks |
| Postgres | Metadata DB |
5️⃣ Install Airflow with Celery + Redis (Docker)¶
📁 Project Structure¶
📄 docker-compose.yml¶
version: "3.8"
x-airflow-common: &airflow-common
image: apache/airflow:2.8.1
environment:
AIRFLOW__CORE__EXECUTOR: CeleryExecutor
AIRFLOW__DATABASE__SQL_ALCHEMY_CONN: postgresql+psycopg2://airflow:airflow@postgres/airflow
AIRFLOW__CELERY__RESULT_BACKEND: db+postgresql://airflow:airflow@postgres/airflow
AIRFLOW__CELERY__BROKER_URL: redis://redis:6379/0
AIRFLOW__CORE__LOAD_EXAMPLES: "false"
volumes:
- ./dags:/opt/airflow/dags
depends_on:
- redis
- postgres
services:
postgres:
image: postgres:15
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: airflow
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: airflow
POSTGRES_DB: airflow
redis:
image: redis:7
airflow-webserver:
<<: *airflow-common
command: webserver
ports:
- "8080:8080"
airflow-scheduler:
<<: *airflow-common
command: scheduler
airflow-worker:
<<: *airflow-common
command: celery worker
airflow-init:
<<: *airflow-common
command: bash -c "airflow db init && airflow users create \
--username admin \
--password admin \
--firstname Admin \
--lastname User \
--role Admin \
--email admin@example.com"
▶️ Start Airflow¶
Access UI:
6️⃣ Your First DAG (Hands-On)¶
📄 dags/example_dag.py¶
from airflow import DAG
from airflow.operators.python import PythonOperator
from datetime import datetime
def hello():
print("Hello from Airflow Celery Worker!")
with DAG(
dag_id="hello_celery",
start_date=datetime(2024, 1, 1),
schedule_interval="@daily",
catchup=False,
) as dag:
task_1 = PythonOperator(
task_id="hello_task",
python_callable=hello
)
task_1
What happens?¶
- Scheduler queues task
- Redis stores message
- Celery worker picks it up
- Worker executes task
7️⃣ Verify Celery Workers Are Working¶
Check worker logs¶
You should see:
🎉 You are now running distributed Airflow tasks
8️⃣ Parallel Tasks Example (Real Practice)¶
from airflow import DAG
from airflow.operators.bash import BashOperator
from datetime import datetime
with DAG(
"parallel_tasks",
start_date=datetime(2024, 1, 1),
schedule_interval=None,
catchup=False,
) as dag:
t1 = BashOperator(
task_id="task_1",
bash_command="sleep 10"
)
t2 = BashOperator(
task_id="task_2",
bash_command="sleep 10"
)
t3 = BashOperator(
task_id="task_3",
bash_command="sleep 10"
)
[t1, t2] >> t3
👉 Watch multiple workers executing in parallel.
9️⃣ Important Airflow CLI Commands¶
# List DAGs
airflow dags list
# Trigger DAG
airflow dags trigger hello_celery
# Test task locally
airflow tasks test hello_celery hello_task 2024-01-01
# Check Celery worker
airflow celery status
🔟 Common Problems & Fixes¶
❌ Tasks stuck in "Queued"¶
✔ Redis not reachable ✔ Worker not running
Check:
❌ ImportError in DAG¶
✔ Missing Python library ✔ Add via custom image or requirements.txt
🔐 Best Practices (Production Mindset)¶
✅ One DAG = one business workflow ✅ Use retries & SLA ✅ Avoid heavy logic inside DAG file ✅ Keep tasks idempotent ✅ Version control DAGs ✅ Monitor with Prometheus / StatsD
🧪 Practice Ideas (Do These Next)¶
- ETL pipeline (API → Transform → DB)
- ML training DAG
- File processing pipeline
- Trigger DAG from REST API
- Add Flower for Celery monitoring
- Add Airflow variables & connections
- Use Redis CLI to inspect queues